The world of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has exploded in popularity and application over the past decade. Once limited to prototyping and hobbyists, 3D printing technology has advanced to allow for finished products, components, medical devices, foods, and more. This disruptive technology has opened up new opportunities for entrepreneurs to start their 3D printing business.
With the right strategic planning and execution, a 3D printing business can be highly successful and profitable. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key steps and considerations for starting your own 3D printing business from the ground up.
Key Takeaways:
- Research 3D printing technology and market demand to assess business potential
- Create a business plan covering costs, services, operations, and marketing
- Obtain funding, register your business, get licenses and insurance
- Buy or lease 3D printer(s) and stock up on materials suited to your offerings
- Develop your brand identity, website, and marketing assets
- Offer services like rapid prototyping, fabrication, and custom 3D printing
- Price competitively and provide excellent customer service for satisfaction
- Leverage social media and SEO to reach new clients and grow your customer base
- Monitor industry trends and upgrade equipment/services to meet demand
- Maintain competitive advantage with quality output, reliable operations, and great service
Understanding the 3D Printing Industry and Market Opportunities
The first step is researching the size and trajectory of the 3D printing industry to assess the market opportunities. According to Statista, the global 3D printing market is projected to be valued at $65 billion by 2029. The market has been growing at a compound annual growth rate of over 15% for the past few years.
With falling costs of 3D printers and materials plus expiring key patents, starting a 3D printing business is more accessible than ever. Well-established players as well as startups are innovating with new 3D printing technologies, materials, and applications. This creates openings in the market to provide specialized 3D printing services.
From a demand perspective, 3D printing adoption continues to accelerate across diverse sectors like engineering and product design, aerospace, healthcare, education, and more. Businesses are utilizing 3D printing for rapid prototyping, fabricating end-use parts, creating customized products, and other applications. This rising demand for quick, flexible, on-demand manufacturing capabilities is fueling the growth of 3D printing service providers.
So if you have experience with 3D printing technology and a business mindset, starting your own 3D printing business can be a savvy move. Careful planning and strategic decisions will be key to competing and succeeding in this evolving industry.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
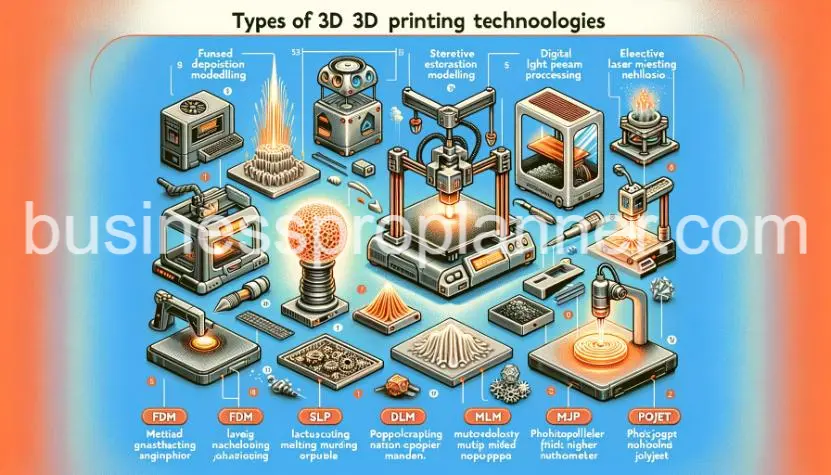
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most common and affordable 3D printing technology. It works by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament through a nozzle onto a print bed layer by layer. Materials used include ABS, PLA, PETG, nylon, and more. FDM offers decent printing speed and is ideal for larger, less intricate prints.
- Stereolithography (SLA) uses a laser to cure and solidify photosensitive resin layer by layer. SLA produces excellent detail and a smooth surface finish ideal for visual prototypes or end products. A variety of engineered resins are available. Post-processing is required to clean supports.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a laser to fuse powdered materials like nylon, glass, and metal powders. It allows the printing of very complex geometries without supports. Parts have excellent mechanical strength. The build chamber is maintained at just below melting point which speeds up sintering.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP) is similar to SLA but utilizes a digital light projector screen to flash light patterns and solidify an entire layer at once rather than tracing with a laser. This increases print speeds significantly.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is a type of powder bed fusion used to 3D print metal parts. An electron beam selectively melts the metal powder in a vacuum and layer-by-layer method. Titanium and nickel alloys are commonly used. It provides extreme hardness and thermal resistance.
- Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) uses an inkjet print head to deposit fusing and detailing agents onto a nylon powder bed. Then the entire layer is uniformly fused with heat. It enables excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surfaces.
- PolyJet uses photopolymer jetting technology to spray ultra-thin layers of photopolymer onto a build tray. The materials are instantly cured by UV light. It enables multi-material printing. Wax and gel supports are used which are later washed away.
Key Steps to Start a Successful 3D Printing Business
Conducting In-Depth Market Research
Before jumping in, you need to thoroughly research the competitive landscape as well as the needs and pain points of potential customer segments. Here are some key aspects to analyze:
- Existing 3D Printing Businesses in your Local Area: Who are the major players? What services do they offer? What are their strengths and weaknesses? How are they positioning themselves and marketing their services?
- Pricing Dynamics: What is the typical pricing for different 3D printing service types based on materials, technologies used, and order sizes? How do competitors price and package their offerings?
- Geographic Gaps: Are there underserved regions where you could establish your business? Factors like access to raw materials and proximity to target customer segments are key.
- Technology Advancements: What new 3D printing technologies are emerging that you could leverage? How can you take advantage of expiring patents?
- Customer Segments: Which industries and professions have a strong need for accessible 3D printing services? Think engineering, manufacturing, industrial design, healthcare, education, retail, etc.
- Specific Customer Needs: What pain points can your 3D printing services solve? Rapid prototyping? Flexible manufacturing? Custom product creation? Identify the top needs you can cater to.
Thorough market research will help you make informed decisions in your business planning process. It will also reveal how to differentiate your business and service offerings to effectively compete.
Creating a Strong Business Plan
Every successful business starts with a robust business plan. This is a detailed document covering your company overview, financial projections, market positioning, operational plans, and more. It will serve as your roadmap for establishing, launching, and growing your 3D printing business.
Here are some key sections to include in your 3D printing business plan:
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of your company, target market, competitive advantage, and projected growth and revenues. This section summarizes the essence of your business plan.
- Company Description: Provides details on your proposed legal structure, location, team, vision statement, and mission statement.
- Market Analysis: Expand on your research of the 3D printing industry outlook, target customer segments, pricing dynamics, and competitive landscape.
- Service Offerings: Describe the specific 3D printing services you plan to provide. For example – rapid prototyping, short-run manufacturing, custom 3D printed products, 3D scanning services, etc.
- Operations Plan: Details your production processes, quality control protocols, software and technologies used, shipping and order fulfillment, safety stock of materials, plans for scaling production, etc.
- Marketing Strategy: Outlines how you will promote your 3D printing services through techniques like content marketing, digital ads, tradeshow participation, direct sales outreach, partnerships, etc.
- Financial Projections: Provides projected income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets, along with supporting assumptions and breakeven analysis.
- Funding Requirements: Specify your needed capital investment to start the business (sourced through loans, investors, etc.) and plans for managing long-term expenses and profitability.
Creating a strong 3D printing business plan will require dedication and attention to detail. But it establishes a roadmap for turning your entrepreneurial vision into reality.
Obtaining Funding to Start Your Business
One of the first obstacles that aspiring entrepreneurs face is obtaining enough capital to start and launch their business. The costs involved in starting a 3D printing business include:
- Purchasing 3D Printer(s): Industrial grade printers can cost $10,000 to $500,000+ depending on size, technologies, and materials capabilities
- Leasing Commercial Workspace and any needed renovations
- Purchasing Raw Print Materials like plastics, resins, metals, etc. You will need to stock up on materials suited to your service offerings. Ongoing material costs must be factored in as well.
- Licenses, Permits, Insurance: Business registration fees, commercial general liability insurance, etc.
- Developing Your Brand Assets: Logo design, marketing materials, website
- Initial Staffing and Employee Salaries: You may need to hire technical staff like 3D printing engineers and designers.
- Other fixed assets like leaseholds, furnishings, hardware/software, etc.
- Working capital needs and Cash Buffer: Enough to cover fixed costs and operating expenses as you scale up.
For most entrepreneurs, self-funding the full costs to start a 3D printing business is a challenge. That’s where securing business financing comes in. Some options include:
- Small Business Administration Loans: SBA 7(a) and 504 loans can provide up to $5 million in low-interest financing for commercial property, equipment, and working capital.
- Business Credit Cards and Lines of Credit: Can help bridge shorter-term financing needs.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo allow you to raise startup funds from a pool of smaller investors.
- Angel Investors and Venture Capital: Pitch your business to private investors for equity financing. Better for larger capital needs.
- Business Accelerators and Incubators: Some provide funding for promising startups meeting their selective criteria.
With strong business planning and financial projections, plus stellar entrepreneurial skills, you can secure the startup funding required to turn your 3D printing business dream into a reality.
Registering Your Business and Obtaining Licenses
Once you have financing secured, you need to take care of business registration, licensing, and insurance requirements. Key steps include:
- Choosing your Legal Structure: Common options like LLC, S-Corp, and C-Corp each have different implications for liability protection, taxation, and raising capital. Consult professionals to determine the best structure for your business.
- Registering your Business Name: You will need to check for name availability and register your business with the state.
- Applying for Federal and State Tax IDs: Required to open business bank accounts, process payroll, file taxes, etc.
- Obtaining Necessary Business Licenses and Permits: Requirements vary based on location and business activities. Research what is needed for operating your 3D printing business legally.
- Securing Commercial General Liability Insurance: Protects against client or third-party claims of bodily injury or property damage. Product liability insurance is also recommended given the nature of your 3D printed outputs.
Purchasing Equipment and Setting Up Your Workspace
One of the most critical investments will be your 3D printing equipment. The printers you choose need to support your planned services and materials capabilities while fitting your budget. Key considerations include:
- Print Technology: FDM/FFF, SLS, SLA, DLP, and PolyJet are leading options, each with pros and cons. Select technologies suited to your target applications.
- Supported Materials: ABS and PLA plastics, photosensitive resins, metals like titanium, aluminum and steel, etc. Ensure your printer can work with your desired materials.
- Build Volume: Bigger is better for higher production capacity but costs are higher too. Choose based on expected order sizes.
- Print Resolution: Measured in microns, tighter resolutions allow highly detailed prints but slower speeds. 0.1 mm is standard.
- Additional Capabilities: Integrated scanners for replicating objects, multi-material and multi-color printing, and networked printing for batch jobs.
- Software: Look for printers with compatible slicer software and apps to prepare files for printing.
- Technical Support: Given the complexities, opt for printers with strong warranties and manufacturer support.
For entrepreneurs starting, leasing printers can be more cost-effective than purchasing. As your business grows, you can invest in buying additional printers or more advanced models. Be sure to budget for ongoing materials costs as well.
Physical Workspace
You will also need to set up your physical workspace. Key requirements are:
- Sufficient space to house your 3D printer(s), post-processing stations, raw material inventory, and workspace for staff.
- Reliable ventilation, temperature control, and exhaust systems. Some materials release fumes during printing.
- Open floor plan layout for workflow efficiency between printers, post-processing, packing, and shipping.
- Electrical supply suited to running your industrial 3D printing equipment. Backup power is ideal to avoid mid-print failures.
- Internet connectivity and local networking between devices.
- Security measures like surveillance cameras if printing expensive client prototypes.
Take time to optimize your workspace layout and workflows before acquiring clients. This will ensure you can deliver reliably from day one.
Developing Your Brand Identity and Online Presence
Like any business, you will need to invest in developing your company’s brand identity and online presence. This is how you present a professional impression to prospects and search engines. Key elements include:
- Branding: Create a distinct but memorable business name and have a logo professionally designed. This will communicate your services and values at a glance.
- Business Website: At a minimum, have a modern website explaining your offerings, capabilities, processes, and methods for contacting you. Prominently display case studies and customer reviews.
- Search Optimization (SEO): Use relevant keywords related to your location and services in page titles, content, URLs, etc. to help prospects find you through local searches.
- Social Media: Set up business pages on LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, etc. Leverage both organic content and paid ads on these platforms to get discovered.
- Marketing Assets: Develop brochures, flyers, signage, and presentations to promote your business at networking events, tradeshows, sales meetings, etc.
- Email Address: Set up a professional email address tied to your domain name for client correspondence and sales inquiries.
Your online presence establishes credibility and discoverability for your new 3D printing venture. A clean, modern brand identity and website convey professionalism and quality to prospects.
Offering Your Planned 3D Printing Services
The core of your business model will be the specific 3D printing services you offer. Assess demand and Konkurrenz123 in your area to determine the best mix of services to launch with. Options include:
- Rapid Prototyping: Producing quick prototype iterations for product designers and engineers to accelerate development processes and test concepts.
- Low-Volume Fabrication: Manufacturing small batches of end-use parts, components, molds, etc.
- Custom 3D Printed Products: Creating personalized 3D printed products like jewelry, mini-figurines, tech accessories, drone parts, board game pieces, etc.
- 3D Scanning Services: Using structured blue light, laser, or CT scanning to digitize objects. The scans are then converted to 3D printable models.
- 3D Model Design: Offering computer-aided design services to turn clients’ concepts into 3D printable files optimized for your printers.
- Contract Manufacturing: Serving as an on-demand production facility for companies needing 3D-printed parts and products.
- 3D Printer Leasing: For clients who occasionally need access to industrial 3D printing equipment without the capital investment.
Carefully assess demand, your capabilities, and potential partnerships to determine the ideal mix of services for starting. You can diversify or scale your offerings over time as the business grows. The goal is to meet your market’s needs better than any competitor.
Pricing Your Services Competitively
Pricing will directly impact the demand you can generate, so research competitive rates in your area and set appropriate prices. Factors influencing 3D printing pricing include:
- Printing Technology and Materials: FDM prints in basic plastics are cheaper than SLA, DMLS, or PolyJet. However exotic 3D printing materials like composites can command premium pricing.
- Labor: Design time, pre-processing, post-processing, and finishing time all add cost. Having trained staff is key to quality results.
- Order Size: Per part costs decrease significantly for batch orders allowing for volume discounts.
- Build Geometry: Structurally complicated prints require more support material and printing time, hence higher pricing.
- Quality and Tolerances: Tighter tolerances and polished surface finishes warrant higher prices.
- Rush Fees: Accelerated turnaround times can attract premium rush order pricing.
- Profit Margins: The profit margin you want to sustain also impacts pricing. But don’t price yourself out of demand.
- Value Differentiation: Premium pricing may be justified for your proprietary technologies, high-end equipment, and stellar service quality.
Adapt your pricing and offer bundling over time based on production costs, order demand, and customer willingness to pay. Running promotions can help attract early customers too.
Providing Excellent Customer Service and Project Quality
Delivering outstanding service quality and project results is critical for securing repeat business and positive word-of-mouth. Some best practices include:
- Assigning each client a dedicated account manager for personalized service.
- Keeping clients updated on project status and any issues requiring feedback.
- Accommodating urgent rush orders whenever feasible, for important clients.
- Meticulously checking finished prints for any defects before shipping.
- Quickly reprinting any objects that get damaged or lost in transit.
- Asking clients to review prints and provide feedback on the full-service experience.
- Honoring any pricing quotes and turnaround time estimates provided.
- Following up after delivery to address any concerns and improve processes.
- Building relationships and trust by understanding each client’s objectives.
By wowing customers and exceeding expectations, you can maximize client retention and positive referrals. These will help fuel stable growth for your 3D printing business.
Leveraging Digital Marketing and Social Media
While traditional marketing remains relevant, digital and social media platforms offer unparalleled reach for promoting your 3D printing business. Here are some of the top options to leverage:
- Search Engine Optimization: Optimizing your website and blog content to rank for relevant local searches like “3d printing services [city]” etc. This delivers a steady stream of prospective clients.
- Paid Search Ads: Running Google/Bing Ads targeted to searches indicating commercial 3D printing needs. Geotargeting nearby regions expands your visibility.
- Social Media Marketing: Promoting your services and showcasing printed objects through Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, LinkedIn, Pinterest and other leading platforms.
- Retargeting Ads: Serving ads to previous website visitors to remind them about your business. This proactively nurtures leads.
- Content Marketing: Publishing in-depth guides, case studies, whitepapers, and other educational content to attract and convert prospects.
- Email Marketing: Collecting emails from site visitors to nurture leads with promotions and helpful content tailored to their interests.
- Industry Forums and Groups: Participating in relevant communities to connect with potential clients interested in 3D printing services.
- Reviews and Referrals: Proactively requesting reviews on Google, Facebook, and industry ratings sites. Referrals should be rewarded.
Executing an omnichannel digital marketing strategy enhances your 3D printing brand visibility and credibility. It will ensure a steady pipeline of prospects discover your business both organically and through paid channels.
Expanding Your Production Capabilities
Starting lean is prudent, but you will need to plan for expanding your 3D printing production capabilities in line with business growth. Here are some proven methods for scaling intelligently:
- Buying Additional Printers: Invest your profits into acquiring newer, faster 3D printing equipment with expanded capabilities as demand grows. Larger build volumes enable higher production throughput.
- Upgrading Printer Technologies: Transition to more advanced 3D printers that enable new materials, better precision, or multi-material printing. This allows you to take on more complex jobs.
- Expanding Your Facility: Lease additional space adjacent to your existing facility and add new printers there. This provides room to scale production capacity.
- Automating Post-Processing: Invest in equipment like chemical baths, tumblers, and sanders to automate smoothing, polishing, and support material removal for consistent quality and faster turnarounds.
- Hiring Specialized Staff: Bring in skilled technicians and engineers tailored to new 3D printing technologies and materials you adopt. Experienced staff ensures optimal quality.
- Introducing New Services: Diversify into new offerings like design services, materials testing, or contracted research to enter new markets and revenue streams.
- Building Customer Loyalty: Nurture loyalty through incentives like expedited turnaround for frequent clients, discounted rates for high-volume projects, and regular check-ins to gather feedback.
- Monitoring the Competitive Landscape: Keep tabs on competitors’ offerings, technologies, and marketing. This allows you to react quickly and differentiate strategically.
- Networking and Community Engagement: Getting involved with local business associations, chambers of commerce, and 3D printing groups strengthens connections with prospective clients.
- Adapting to Evolving Technologies: Evaluate new 3D printing technologies regularly. Adopt innovations offering tangible benefits and ROI for your business model and clients.
By scaling your operations in step with demand, you can maximize the growth potential of your 3D printing business and continue delighting customers.
Maintaining Quality and Competitive Advantage
Success ultimately hinges on maintaining quality, reliability, and competitive advantage. Follow these tips:
- Obsess Over Quality: Rigorously inspect prints before delivery and quickly address any client complaints. Your reputation depends on it.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Don’t stretch yourself thin. Build on strengths rather than adding services indiscriminately.
- Leverage Partnerships: Partner with design firms, materials suppliers, and other specialists to expand your capabilities.
- Reinvest Continually: Allocate profits to upgrading equipment, technologies, and staff skills. Stagnation means falling behind.
- Monitor Market Signals: Stay on top of emerging client needs you should prepare for through R&D and pilot projects.
- Solicit Client Feedback: Act on feedback from surveys and reviews to fine-tune processes, quality, and internal communication.
- Reward Employee Initiative: Motivate staff to suggest improvements and contribute ideas that help the business stay competitive.
By delivering an amazing customer experience powered by strategic investments and a motivated team, your 3D printing services business can thrive for the long haul.
Monitor Trends and Innovate
Staying abreast of emerging technologies and applications for 3D printing helps ensure your business remains relevant and progressive over the long run. Some future developments may include:
- Advanced multi-material printing and nanoscale resolution
- Large-scale additive manufacturing for construction and architecture
- The rise of 3D bioprinting of human tissues and living structures
- Integrated artificial intelligence to automate 3D design and production
Consider taking online courses to gain expertise in cutting-edge areas as capabilities evolve. Pilot new offerings like 3D printed electronics or precision healthcare models to stay ahead of your competition.

Conclusion
Launching a new business in 3D printing lets you tap into the expanding world of additive manufacturing, igniting your entrepreneurial spirit. Begin your 3D printing journey with strategic planning and wise investments. Moreover, excellent marketing and a strong focus on client satisfaction are key to growing your business.
Use 3D technology effectively, whether in a home-based setup or a larger operation. Additionally, starting your 3d printing business can involve diverse services like printing prototypes and manufacturing components. This approach, combined with dedication, paves the way for a successful venture. Follow this simple yet effective roadmap to turn your 3D printing business into a thriving success.
Muhammad Asif Saeed has extensive experience in commerce and finance. Specifically, He holds a Bachelor of Commerce degree specializing in Accounts and Finance and an MBA focusing on Marketing. These qualifications underpin his understanding of business dynamics and financial strategies.
With an impressive 20-year career in Pakistan’s textile sector, including roles at Masood Textile (MTM) and Sadaqat Limited, excelling in business & financial management. His expertise in financial and business management is further evidenced by his authoritative articles on complex finance and business operation topics for various renowned websites including businessproplanner.com,businesprotips.com,distinctionbetween.com, trueqube.com, and bruitly.com, demonstrating his comprehensive knowledge and professional expertise in the field.

1 thought on “How to Start a 3D Printing Business – From Concept to Reality!”