Understanding the process of guiding business strategy using facts is pivotal in today’s data-centric world. Nowadays, every business needs to use data to guide the way forward in an increasingly complicated world. Basing a strategy on analytics and facts has become essential, not optional. Leading companies know relying on gut feel instead of data puts them behind.
The way ahead is to gather insights from all teams, spot key patterns, and use those to shape plans. With the right focus on data, businesses can make choices based on evidence rather than guesses.
But this requires all employees to adopt a mindset that values facts over hunches. In this blog, we will share how organizations can bake analytics into their culture and move ahead guided by what the data shows. The companies that get good at this will pull ahead of the rest.
What is data-driven decision-making?
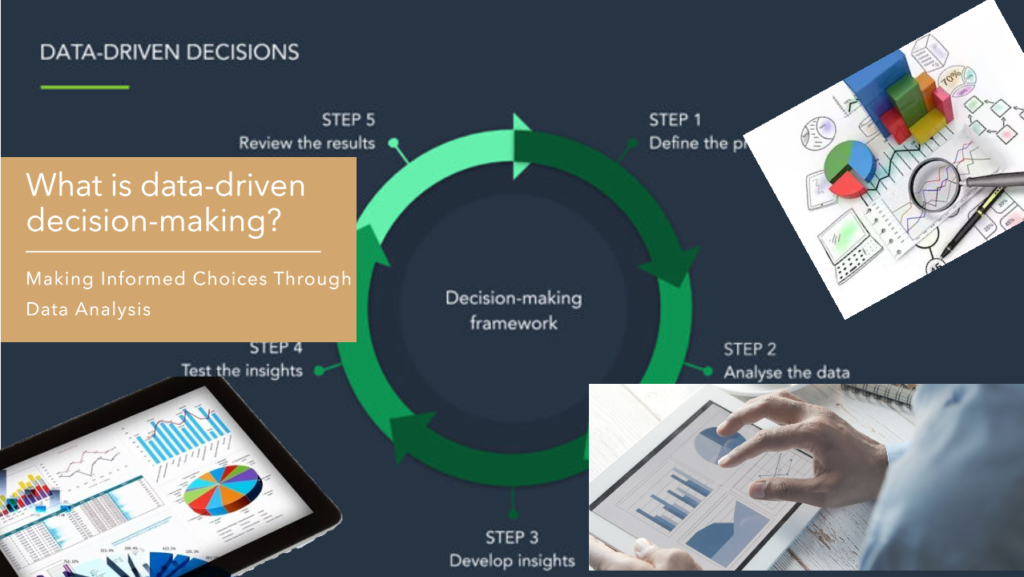
Here’s the thing – today’s organizations need to tap into the power of data to guide their game plan, much like GPS guides drivers. Data-driven decision-making refers to the process of guiding business strategy using facts and evidence-based information.
This means pulling together relevant info from across the business. analyzing it to extract meaningful insights, and then using those aha moments to inform major moves and solutions. When done right, companies can mine the data to reveal guideposts that point the way toward smart decisions and future success.
But this is not about gawking at spreadsheets packed with numbers. True data-driven decision-making means grasping the bigger picture story behind the metrics. It’s about reading between the lines to understand what the data is whispering and then having the courage to align actions with that evidence-based narrative. Companies that can master this analytical art of letting the data lead will be poised to outpace the competition.
Why Fact-Based Strategy Matters in Business?
Let’s get real – basing strategic plans on gut feel and finger-in-the-wind observations is no longer enough in today’s data-driven world. Companies that don’t make analytics their trusty co-pilot risk being left in the dust. Embracing the process of guiding business strategy with facts paves the way for informed success and market leadership.
Leading organizations know leveraging data is now mission-critical. Here’s why:
- Data analysis illuminates emerging opportunities, market shifts, and smart investments others may miss. It provides a clear-eyed view of the competitive landscape.
- Customer analytics and sales data reveal product gaps, pain points, and changing needs to address.
- Metrics expose problem areas and bottlenecks. Data shows where to focus improvement efforts for maximum impact.
- KPI dashboards allow leaders to continuously track progress on strategic goals. Rapid iteration becomes possible.
- Analytics enables quick pivots as market conditions evolve. Data fuels smarter, more agile strategy settings.
The bottom line is a data-driven approach provides much-needed focus and factual grounding to create winning strategies tailored to your organization’s specific objectives. Companies that leverage their power will soar past those relying on instinct alone.
Different Types of Data: Fueling Business Strategy with Facts
In today’s evolving business landscape, the growth of a company is anchored in its talent for collecting and understanding data. Cultivating a data-focused mindset isn’t a fleeting trend, but a fundamental pillar for long-term success. By using facts to guide business strategy, organizations ensure their strategy is grounded in reality, offering them a tangible competitive advantage.
Let’s explore the various types of data essential for making fact-based decisions:
- Quantitative Data: These are the raw numbers—the sales numbers, percentages, and KPIs. For instance, understanding that a store earns 15% more in one quarter compared to another provides a quantitative perspective on performance.
- Qualitative Data: This encompasses feedback, opinions, and subjective information. When a customer narrates their customer experience or an employee realizes that since a new policy was implemented. Morale has improved, that’s qualitative data in action.
- Primary Data: Firsthand, original data collected by the organization, such as direct customer feedback or user behavior on a new product.
- Secondary Data: Information derived from external sources. This can be market research reports, competitor analysis, or industry trends, offering insights into broader market trends and positioning.
- Big Data: Extensive datasets need special tools for analysis. Skilled analytics teams can find patterns, and opportunities, and predict trends.
- Visual Data: Visual Data: This includes things like charts, pictures, and simple graphics. Effective data visualization translates complex data into easily digestible visuals, aiding in quick decision-making for stakeholders.
By integrating data and analytics into the core business model, organizations not only stay ahead of the curve but also ensure that every strategic move is backed by empirical evidence.
The Advantages of Data-Informed Decision Making

Enriched Business Strategy Formulation
- Adopting an analytics-focused culture ensures strategy aligns with reliable data, making choices more result-driven.
- Data insights provide key guidance to chart an organization’s future course, illuminating the pathway ahead.
Precise Decision-Making
- Deciding with facts minimizes guesswork, ensuring options sync with business objectives.
- Analysts can decode data sources, grounding choices in robust evidence.
Streamlined Operations
- Data-guided decisions optimize day-to-day activities, smoothing workflows.
- Analytics tools like dashboards and BI software identify process bottlenecks.
Unified Stakeholders
- Guiding strategy with data-backed insights unifies stakeholders, as the empirical basis is clear.
Sustained Competitive Edge
- Analyzing competitor and market data powers proactive responses, maintaining advantages.
- With data foresight, firms can get ahead of industry shifts.
Optimized Resource Allocation
- Data focus ensures resources are invested where they will deliver maximum impact and ROI.
- Analytics help calibrates budgeting to avoid waste.
Tailored Customer Experiences
- Data illuminates customer preferences, enabling refined offerings for greater satisfaction.
Empowered Employees
- Developing data fluency Makes teams more self-sufficient and informed, improving morale.
- An enabled analytics organization catalyzes innovation company-wide.
Risk Reduction
- Data-based choices minimize missteps.
- Contextual insights and technical acumen identify potential pitfalls.
Financial Return
- An analytics focus frequently improves sales and efficiency, benefiting the bottom line.
Different methods of data analysis:
In the day-to-day activities of any modern organization, data-driven decision-making is pivotal in guiding business strategy using facts. By using facts to guide business, stakeholders can ensure that their strategy is grounded in reality and can propel the business forward towards its objectives. Here are the key methods:
Statistical Analysis
- Regression analysis to identify correlations
- Time series analysis for trends and forecasts
- ANOVA analysis for differences between groups
- Optimization modeling for ideal scenarios
Data Mining Techniques
- Clustering data into meaningful segments
- Association rules to uncover relationships
- Anomaly detection to identify outliers
- Pattern recognition through neural nets
Sentiment & Text Analysis
- Natural language processing of unstructured data
- Social media monitoring for brand sentiment
- Competitor textual content analysis
Predictive Modeling
- Forecasting future outcomes and trends
- Predictive analytics to guide planning
- “What-if” scenario modeling for preparedness
Data Visualization
- Charts, graphs, and maps to spot patterns
- Dashboards with KPIs for real-time tracking
- Interactive visualizations for engagement
By centralizing data with tools like business intelligence (BI) management software. Businesses ensure accurate data sources, aligning their data strategy with objectives for a competitive advantage.
The Process of Data-Driven Decision-Making
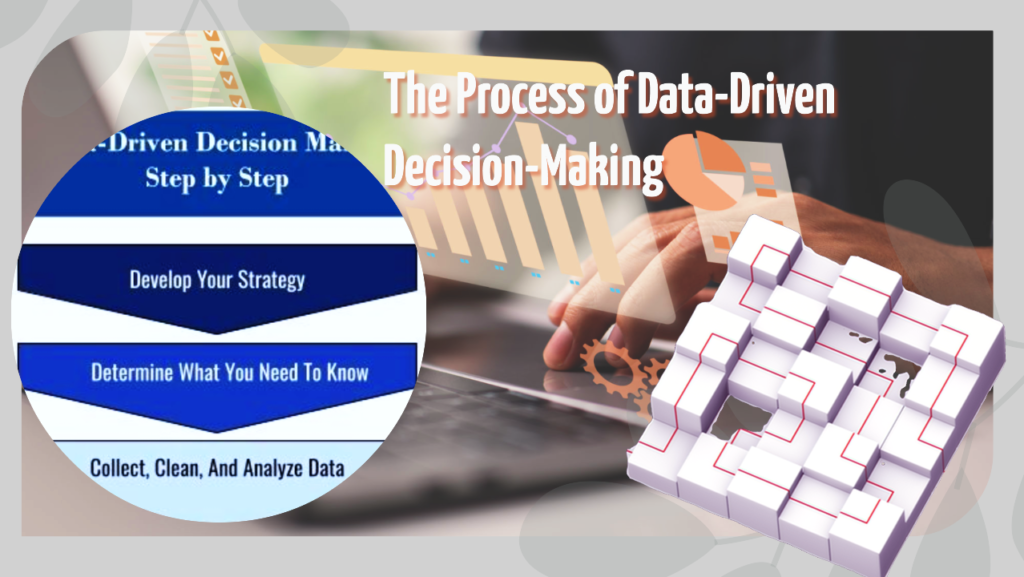
Clearly Define the Strategic Business Objective
- Articulate the specific business issue, question, or growth opportunity
- Set quantifiable KPIs and success metrics aligned with goals
- Focus efforts on collecting and analyzing directly relevant data
Compile Applicable Internal and External Data
- Gather cross-functional internal data on operations, sales, HR, finances
- Conduct customer surveys, interviews, and focus groups for qualitative insights
- Leverage business intelligence systems to efficiently consolidate data
- Research external data like industry benchmarks, market reports, and trends
- Contextualize internal data with big-picture perspectives
- Ensure data relevance to defined strategic objective
Conduct Rigorous Data Analysis
- Perform statistical analysis to uncover correlations, patterns, and trends
- Apply data mining techniques to identify deeper relationships and segments
- Develop predictive models and forecasts to inform forward-looking strategy
- Visualize data through charts, graphs, and dynamic dashboards
- Synthesize raw analytics into strategic insights and recommendations
- Translate technical findings into a business context for decision-makers
- Identify data-driven opportunities, risks, and solutions to pursue goals
Make Objective Data-Aligned Decisions
- Weigh analytical insights with pragmatic judgment and expertise
- Evaluate data-backed pros and cons of potential choices
- Select options optimized to achieve the defined business objective
- Balance data guidance with practical limitations
- Ensure decision alignment across the leadership team
- Document the rationale behind the choice for future reference
Continuously Monitor Results and Optimize
- Track relevant KPIs to monitor performance over time
- Input updated data into analytical models for ongoing optimization
- Identify positive and negative variances from the plan
- Refine approach continuously based on the latest metrics
- Ongoing measurement, evaluation, and improvement cycle
Examples of Data-Driven Decision-Making in Business
Identifying Market Trends
- Analyze sales data, web metrics, and customer demographics using statistical analysis to reveal demand trends
- Incorporate external market research data to contextualize insights and identify growth opportunities through competitive analysis
- Guide strategic planning and resource allocation decisions based on data-derived market intelligence
Targeting Marketing Efforts
- Collect customer usage and engagement data and segment by attributes using data mining techniques
- Track marketing campaign KPIs like click-through rate and conversions and optimize spend through data modeling
- Tailor messaging and offers using predictive analytics based on customer lifetime value data
- Focus high-touch marketing efforts on high-value segments identified through clustering analysis
Improving Product Development
- Apply statistical analysis and data visualization to identify customer needs and pain points in survey data
- Mine user feedback, reviews, and focus group transcripts for common feature requests
- Build minimum viable products (MVPs) to test with focus groups and rapidly iterate based on usage metrics
- Use conjoint analysis to inform pricing strategy and packaging design grounded in data insights
- Forecast sales volumes based on analogous product launch data using predictive analytics
Reducing Costs
- Identify highest spend areas using spend analytics and uncover savings opportunities through data mining
- Assess supplier rates compared to industry benchmark data to negotiate better contracts
- Detect process inefficiencies by analyzing operational and supply chain metrics
Increasing Profits
- Optimize pricing strategy using price elasticity modeling, customer willingness-to-pay data, and segmentation analysis
- Identify high-margin products through product profitability analysis to prioritize resources
- Enhance customer lifetime value through targeted cross-sell and upsell driven by data insights
- Develop data-driven growth strategies tailored to revenue goals based on statistical forecasting
The Challenges of Data-Driven Decision-Making
While the process of guiding business strategy using facts is a powerful approach, it’s not without its hurdles. Here are some challenges businesses might encounter:
Quality of Data Sources:
- Reliable data sources are the backbone of data-driven decision-making.
- However, not all sources provide accurate and relevant data. Inaccurate data can misguide a business strategy.
Over-reliance on Data:
- While data-driven insights are vital, solely relying on data without considering the human aspect can be problematic.
- Decision-making is using facts, but intuition and experience still play a role.
Complexity of Data Analysis:
- With vast amounts of data available, the data analysis process can be overwhelming.
- It requires specialized data skills and tools for accurate analytics.
Cultural Barriers:
- Establishing a data-driven culture across the organization can be challenging.
- Employees might resist changing their decision-making habits.
Technical Challenges:
- Implementing business intelligence and analytics tools requires a technical mindset.
- Integration issues with existing systems can arise, potentially hampering the data strategy.
Security Concerns:
- As businesses centralize their data, it becomes a critical enterprise asset.
- Protecting this data from breaches is paramount.
Interpreting Data Correctly:
- Data visualization can simplify complex data sets. However, without a proper understanding of the context, misinterpretation is possible.
Skill Gap:
- Not every organization has access to a skilled analytics team or data analyst.
- Training employees to learn about data and tools is essential but can be time-consuming.
Overhead Costs:
- Investing in data and analytics tools, systems, and training might increase initial overheads before businesses see a return on their investment.
By understanding these challenges, businesses can better prepare and refine their data-driven approaches, ensuring their strategy is grounded in both facts and practical considerations.
How to Overcome the Challenges of Data-Driven Decision-Making
Making sense of decisions based on data can seem tough, but with the right plan, businesses can truly tap into the value of their data.
Investing in Robust Data Sources
- Make acquiring consistent, high-quality data a priority. Ensure collected information remains relevant and current.
- Basing choices on facts necessitates precise, vetted facts.
Counterbalancing Data with Human Insights
- While analytics offer invaluable direction, balance data-derived insights with human intuition and experience.
- This holistic approach produces a nuanced strategy.
Training and Enhancing Data Fluency
- Invest in developing personnel’s data analysis acumen and proficiency with tools.
- Enable an organization-wide data-focused culture through upskilling.
Leveraging Cutting-Edge Analytics Technology
- Empower analytics teams with advanced tools that streamline insight extraction.
- Data visualization catalyzes rapid, accurate intelligence.
Fortifying Data Security
- Safeguard data integrity by implementing robust cybersecurity and access controls.
- A sound data strategy necessitates uncompromised information assets.
Tapping External Perspectives
- Engage third-party data scientists who contribute specialized expertise and fresh outlooks.
Adopting an Agile Approach
- Take an iterative approach to data-guided decision processes.
- Continuously integrate new inputs and feedback to refine strategy.
Incorporating Stakeholder Feedback
- Create feedback channels to anchor strategy in real-world considerations.
- Input connects decisions to business objectives.
Remaining Updated
- The data analytics landscape progresses swiftly. Stay current with innovations.
By proactively addressing these challenges, businesses can ensure that their process of guiding business strategy using facts remains efficient, effective, and in line with their broader objectives.

Wrapping Up
In today’s highly competitive business environment, making decisions using data isn’t just a good drive-thru idea—it’s needed to succeed. Companies that use a clear method to gather, understand, and use data can make better plans and work choices based on real evidence. Yes, it can be hard, but the benefits are big.
Data is like a map that helps companies find the best way forward, use resources wisely, and reach their goals. Leaders who use data to make choices stand out from the crowd. Staying dedicated to using data to get better can be hard, but the benefits of growing this way are too important to overlook in today’s business scene.
Muhammad Asif Saeed has extensive experience in commerce and finance. Specifically, He holds a Bachelor of Commerce degree specializing in Accounts and Finance and an MBA focusing on Marketing. These qualifications underpin his understanding of business dynamics and financial strategies.
With an impressive 20-year career in Pakistan’s textile sector, including roles at Masood Textile (MTM) and Sadaqat Limited, excelling in business & financial management. His expertise in financial and business management is further evidenced by his authoritative articles on complex finance and business operation topics for various renowned websites including businessproplanner.com,businesprotips.com,distinctionbetween.com, trueqube.com, and bruitly.com, demonstrating his comprehensive knowledge and professional expertise in the field.


nice content!nice history!! boba 😀
nice content!nice history!! boba 😀
🌟 This post is like finding a hidden treasure! 🌟